Why Does the Disk Not Have Enough Space to Replace Bad Clusters
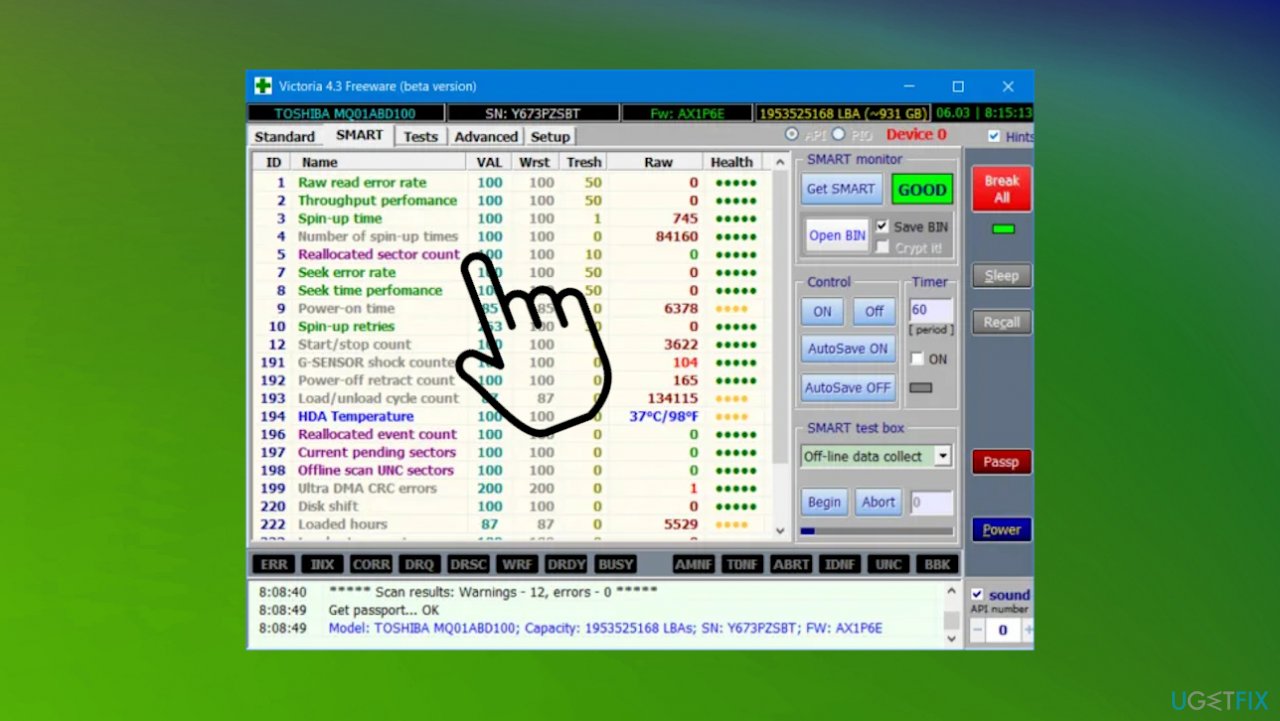
In the event that a disk does not contain enough space to repair poor clusters, this refers to the situation in which the storage device comes across affected or damaged areas, referred to as bad clusters.
However, there’s insufficient space for replacement with health clusters.
Clusters that are bad are areas of the surface of the disk that have developed a fault and are not able to hold or retrieve the data in a proper manner.
If a disk discovers it as a bad cluster it will attempt to recreate it using an appropriate cluster from an allocated collection of clusters that are spare.
But, if there’s not enough space left on the disk for this process, the damaged cluster will remain not repaired.
This can result in files being corrupted, data loss, and instability of the system since the operating system will be incapable of writing or reading information to the affected area efficiently.
Insufficient space to repair bad clusters could result from a number of causes the disk is nearing its capacity, fragmentation of the disk, or excessive use.
If the problem isn’t resolved quickly, it may result in further deterioration of the performance of the disk. It could need professional assistance to save your data and restore the disk.
To avoid encountering the issue regularly, disk maintenance, regular backups of data, as well as timely check-ups on the disk are crucial to ensure the performance and health of your storage device.
What are the Main Causes of the disk does not have enough space to replace bad clusters
Disk Overutilization: When a disk gets frequently used and is almost fully staffed, there may not be enough space for the replacement of the bad clusters. A lack of space hampers the ability to map the affected areas to healthy clusters. This results in clusters with bad connections that cannot be resolved.
Disk Fragmentation: As the data gets written down deleted or moved about the disk it may get fragmented. The fragmentation of files spreads across various parts of the disk making it difficult to find enough space for the replacement of clusters that are damaged. This could result in the disk not being able to make enough space available to remap.
Hardware and Software issues: Malfunctioning software or hardware issues can lead to issues with the disk management procedure. In certain instances, they can also interfere in the process of distributing free space needed to repair damaged clusters and prevent repair work to be completed.
Physical Disk Damage: Physical damage to the disk, like cracks or mechanical problems, may result in the development bad clusters. If this occurs it is possible that the disk does not be functional enough for the repair process efficiently.
Insufficient disk maintenance: Failure to carry out regular maintenance of your disks like disk cleaning and defragmentation, may cause the problem of not having enough space. The disk builds up in excess files and fragments there is a greater chance of having inadequate space to support poor cluster replacement increases.
Power Sustained Shutdowns and Surge Power: Unexpected power surges or abrupt system shutdowns could result in disk failures as well as the formation of clusters that are not optimal. Such events can leave the disk in a fragile condition and hamper the replacement of damaged clusters.
Why this Occurs
The issue of disks not being able to be able to substitute bad clusters could be explained by a variety of factors:
- Disk Overutilization A most common reason is when the disk is being used extensively nearing its capacity of storage. Since the disk gets filled with information, there could not be enough space left to fund replacing bad clusters. This limits the capability of the disk to replace affected areas with healthy clusters.
- Fragmentation As information is written down, erased, and moved about in the storage device, it may be broken up. It scatters data across many regions of the disk making it difficult to find enough space for the replacement of clusters that are damaged. In turn, the disk could be unable to locate enough room for remapping.
- Unresolved Disk Problems: If the disk is already contaminated with errors, or bad clusters which weren’t successfully substituted in prior attempts The space available for mapping to new bad clusters could be reduced further.
- Inadequate Maintenance Inadequately performing regular maintenance activities, including cleaning and defragmenting the disk may increase the size of space. The disk builds up in excess files and gets fragmented and cluttered, which decreases the chance of having enough space available to replace a bad cluster.
- Hardware and Software Problems: Malfunctioning software or hardware problems can result in problems with the disk management procedure. These problems can hinder the allocation of available space needed to replace clusters that are damaged and result in clusters not being resolved.
- Physical Disk Damage: Physical damage to the surface of the disk, for example, damage from mechanical or physical failures could result in bad clusters. If this occurs it is possible that the disk does not be functional enough for the process of replacement successfully.
- Power Interruptions Power surges that are sudden or system shut-downs that are sudden can result in disk failures as well as the formation of clusters that are not optimal. Such events could leave the disk unstable and prevent the correct replacement of damaged clusters.
How to Fix the Disk Does Not Have Enough Space to Replace Bad Clusters
The discovery of bad clusters on your disk is a concern, when there’s not enough room to swap them out this can cause additional issues and even data loss. In this thorough tutorial, we’ll guide you through the steps to repair the disk when it doesn’t have enough room to substitute poor clusters.
Step 1: Check Disk Space
Before you attempt any repairs before attempting any fixes, you must verify the disk space available in your drive. How to do that:
- For Windows: Open File Explorer Click on the disk you’d like to examine, then select “Properties,” and view the space that is available.
- To Access on Mac: To access the Mac Apple logo at the top left corner. Choose “About This Mac,” click “Storage,” and review the available storage space.
If your space for use is not enough, you’ll require to release the space prior to dealing with poor clusters.
Step 2: Deleting Unneeded Files
Remove any unwanted files like the temporary files, downloads from years ago, or other files you don’t require. This can help you to free up space on your disc. Here’s how:
- In Windows On Windows: Open “Start” on Windows. Click the “Start” menu, then select “Settings” Then, click “System” and then “Storage” and click on “Temporary files” or “Free Space Now.”
- For Mac Start Finder on your Mac and click “Go” from the menu bar. Select “Go into Folder,” type “~/Library/Caches” and then delete any unnecessary files. In addition, you should empty your junk to make storage space.
Step 3: Perform Disk Cleanup
Both Windows as well as Mac both have built-in disk clean-up tools that can help you get rid of unwanted files in to left area. How to utilize the tools:
- For Windows On Windows: Type “Disk Cleanup” within the Start menu. Choose the disk that you wish to clear, and then follow the steps to eliminate unwanted documents.
- Use Mac: Use the “Optimize Storage” feature to tidy up your drive in a timely manner. Click on Apple Menu >> About This Mac > “Storage” > “Manage,” and click on “Optimize” to initiate the cleaning process.
Step 4: Remove the Program That you Have Not Used
Deleting any program or application which you do not use since they are filling up your disk space with unnecessary data. Here’s how:
- In Windows You can go to “Start” and then “Settings” and then “Apps,” scroll through the list of apps installed and select those you’d like to eliminate then select “Uninstall”.
- For Mac, You can simply drag undesirable programs from the “Applications” folder into the garbage.
Step 5: Disk Defragmentation (Windows)
If you’re running the traditional hard drive (HDD) running Windows think about defragmenting your disk. The process helps to organize the information stored on the disk, making it simpler to assign the space needed for replacements of bad clusters.
- Find “Defragment Optimize and Defragment Drives” within the Start menu Select the drive, and then click “Optimize” to initiate the process of defragmenting.
Step 6. Utilize the Disk Tool (Mac)
When using on a Mac You can utilize The Disk Utility to test and fix disk issues such as poor clusters.
- Open “Applications” > “Utilities” > “Disk Utility”.
- Pick your Drive on the Left Side.
- Select “First Aid,” then click on the “First Aid” tab. Then select “Run” to start the repair procedure.
Step 7: Check Disk for Errors (Windows)
For Windows On Windows, you are able to use Check Disk on Windows. Check Disk utility to detect and fix disk issues which include bad clusters. Here’s how:
- Start Command Prompt in the administrator mode Click on Start, right-click and select the menu and select “Windows Terminal (Admin)” or “Command Prompt (Admin).“
- Enter the command below and then press Enter: chkdsk/f
- There could be a notification saying that the disk is currently being used and a request for permission to make an inspection on the next reboot. Enter “Y” and hit Enter.
- Start your computer and then the Check Disk utility will run to repair any issues.
Step 8: Backup Important Data
Prior to attempting any repairs on your disk prior to attempting any disk repairs, you must backup your information to an external drive or cloud storage in order to avoid losing your data.
Make use of external hard drives USB flash drives, and cloud-based services such as Google Drive or Dropbox for this reason.
Step 9: Think About the Assistance of a Professional
If your disk doesn’t provide enough space for replacing damaged clusters even after following these steps It could be the right time to seek assistance from a specialist in data recovery or an IT professional.
They have the experience and equipment to deal with difficult disk problems without risking the loss of data.
Be aware that fixing clusters with bad performance needs careful consideration to avoid losing data. Always ensure that your data is backed up prior to trying any repair. If you’re not sure of the repair yourself, it’s recommended to seek out a professional’s assistance and guidance.