You might or may not have heard of prompt engineering. In essence, it’s communicating with an AI to obtain the results you desire’.
The majority of people don’t like the speed of engineering
But, it’s becoming more and more crucial skill…Because garbage in equals garbage out.
Here are the most crucial methods you can use to prompt
The term I’ll use to describe a model of language by the name “LM”.
Some examples of language models include the @OpenAI‘s ChatGPT as well as the @AnthropicAI‘s Claude.
1. Personal/role prompting
Delegate a job to AI. AI.
Examples: “You are an expert in X. You’ve assisted people in doing the Y task for more than 20 years. Your job is to provide the most effective advice on X.
Respond with ‘got it’, in the event that you understand.”
An effective add-on is:
You must always inquire before answering to ensure you understand what the person asking questions.’
I’ll discuss why this is so crucial in a moment.
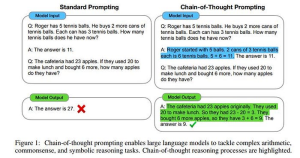
2. CoT
CoT is a contraction of “Chain of Thought’
It’s used to train the LM to provide its reasons.
Example:
3. Zero-shot-CoT
Zero-shot is a term used to describe a model that makes predictions with no further training in the prompt.
I’ll be able to shoot a few shots within a few minutes.
It is important to note that CoT usually > Zero-shot-CoT
Example:
4. Few-shot (and few-shot-CoT)
Few-shot occurs when the LM is provided with a few examples to prompt it to be able to quickly adapt to new situations.
Example:
5. Knowledge Generation
The generation of knowledge related to questions is accomplished through inducing an LM.
This can be used as an generated knowledge prompt (see more).
Example:
6. The Knowledge Gained is Accumulated
Once we know and information, we can put the information into a new prompt, and then pose questions based on the information.
A question like this is referred to as”knowledge-augmented” questions.
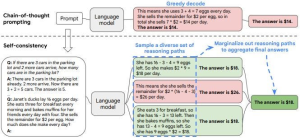
7. Self-Consistency
This method is employed to create multiple reasoning pathways (chains of thinking).
The majority of answers are taken to be the final answer.
Example:
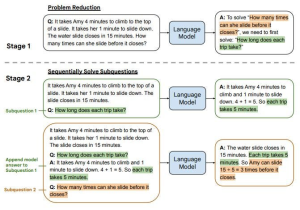
8. LtM
LtM is a reference to ‘Least to Most’
This method is a follow-up to CoT. It also is based on breaking the problem into smaller ones and then solving them.
Example: